
Our product portfolio includes Smart-NLD for non-lethal wildlife deterrence, AI-based image analysis software for ecological monitoring, and Soundscapes for rapid biodiversity assessment, demonstrating our commitment to technical progress and innovation in environmental science and technology.
PRODUCTS
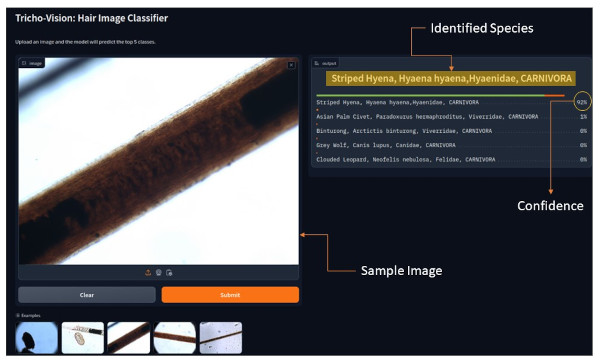
TRICHO-VISION
SMART NLD

OUR WORKS


Individual Identification of Clouded Leopards Using AI-Based Technology
Project Overview: This project aimed to quantify the number of distinct clouded leopards within Buxa Tiger Reserve, West Bengal, India, using strategically placed camera traps. The primary challenge was accurately identifying and differentiating individual leopards based on their unique stripe and marking patterns.
Innovative Technology: To address this challenge, we implemented a robust pattern matching strategy using cutting-edge AI technology, including:
- Super-Point Algorithm: Used for key point detection, this self-supervised algorithm adapts to variations in scale, rotation, and lighting conditions, generating distinctive feature descriptors from leopard images.
- Super-Glue Algorithm: Utilizing graph neural networks and attention mechanisms, this algorithm accurately matched patterns to identify individual leopards, ensuring precise results by focusing solely on unique markings and excluding background interference.
- Segmentation Masks: Generated to isolate leopards from the background, enhancing the accuracy of the pattern matching process.

Tricho-Vision serves as a pioneering tool that leverages advanced computer vision to identify mammalian species based on microscopic hair characteristics, addressing crucial challenges in wildlife conservation and forensic science. By analysing hair cuticle patterns, medulla structure, and other key features using machine learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs), the framework provides accurate identification across taxonomic levels, from species to order. This ability aids law enforcement agencies in curbing wildlife crime, supports researchers in studying biodiversity, and enhances conservation strategies for species at risk. The Tricho-Vision framework demonstrates the power of artificial intelligence in wildlife protection, serving as a vital resource for monitoring biodiversity, investigating wildlife crime scenes, and understanding ecosystem dynamics. Its application ensures that endangered and protected species receive the attention needed for survival and enforcement of international conservation laws.



Individual Identification of Clouded Leopards Using AI-Based Technology
Project Overview: This project aimed to quantify the number of distinct clouded leopards within Buxa Tiger Reserve, West Bengal, India, using strategically placed camera traps. The primary challenge was accurately identifying and differentiating individual leopards based on their unique stripe and marking patterns. Innovative Technology: To address this challenge, we implemented a robust pattern matching strategy using cutting-edge AI technology, including:- Super-Point Algorithm: Used for key point detection, this self-supervised algorithm adapts to variations in scale, rotation, and lighting conditions, generating distinctive feature descriptors from leopard images.
- Super-Glue Algorithm: Utilizing graph neural networks and attention mechanisms, this algorithm accurately matched patterns to identify individual leopards, ensuring precise results by focusing solely on unique markings and excluding background interference.
- Segmentation Masks: Generated to isolate leopards from the background, enhancing the accuracy of the pattern matching process.